3.stack
栈,继承Vector类,构造函数就是只有默认构造函数,构造空栈。
package vector;import java.util.Enumeration;import java.util.Stack;public class StackClass {public static void main(String []args){ Stack st=new Stack (); empty()和isEmpty()一毛一样 System.out.println(st.empty()); System.out.println(st.isEmpty()); for(int i=0;i<10;i++) st.add("1"+i); for(String j:st) System.out.print(j+" "); System.out.println(); /*pop*/ 压入栈,返回这个值 System.out.println(st.pop()); /*push*/ 弹出栈,返回这个值 System.out.println(st.push("I'm")); System.out.println(st.push("Stack")); /*peek*/ 返回栈顶 System.out.println(st.peek()); Enumeration e=st.elements(); while(e.hasMoreElements()) { System.out.print(e.nextElement()+" "); } System.out.println(); /*search*/ search倒着数的。。。 System.out.println(st.indexOf("18")); System.out.println(st.search("18"));}}
4.LinkedList
空构造函数和以Collection为参数的构造函数。
API函数:
boolean add(E object) void add(int location, E object) boolean addAll(Collection collection) boolean addAll(int location, Collection collection) void addFirst(E object) #####void addLast(E object) #####void clear()Object clone()boolean contains(Object object)IteratordescendingIterator() #####E element() //等於getFirst(),具體實現一樣E get(int location)E getFirst() E getLast()int indexOf(Object object)int lastIndexOf(Object object)ListIterator listIterator(int location)boolean offer(E o) ####等于add、addFirst、addLastboolean offerFirst(E e) ####boolean offerLast(E e) ####E peek() ##########E peekFirst() #########E peekLast() #######E poll() #########E pollFirst() ############E pollLast() #######E pop() ######void push(E e) #######E remove()E remove(int location)boolean remove(Object object)E removeFirst() ##boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) ##E removeLast() ##boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) ##E set(int location, E object)int size() T[] toArray(T[] contents)Object[] toArray()
基本上没有什么可以讲解的了,值得注意的是两套增加、删除和访问头和尾的,以下转自博客园博主 “如果天空不死”
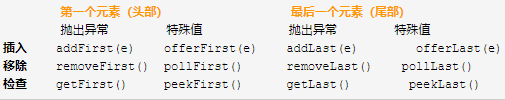
其中poll()有和pollFirst()相同,与remove()对应;peek()与peekFirst(),与get()对应;offer()与add()类似。
那么剩下只有descendingIterator()、removeFirstOccurrence()和removeLastOccurrence()了,descendingIterator与iterator完全相似(不是ListIterator,因为没有previous的方法),只是从后往前的迭代器。removeFirstOccurrence与remove完全相同,还与pop相同。注:push()与addFirst()完全相同。。。
就剩下一个了removeLastOccurrence,作用是在链表中移除最后一个出现的该参数。
以代码来详细分析一下add(int index,E element)
public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } 先来看checkPositionIndex()方法就是为了防止index出界,出界就抛出异常。
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { if (!isPositionIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index <= size; } 如果没越界,那判断是不是末尾,如果是使用LinkLast()方法将元素插到末尾,否则使用LinkBefore()插入到中间
/** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node l = last; //将末尾节点赋给l final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //申请一个新的节点,prev是l,next是null last = newNode; //将新节点变为末尾节点 if (l == null) first = newNode; //l是null代表链表为空,那么头节点也是末尾节点 else l.next = newNode; //否则l连接新节点 size++; modCount++; } /** * Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. */ void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) { // assert succ != null; final Node pred = succ.prev; final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); //申请一个新的节点,prev是pred,next是succ,元素是e succ.prev = newNode; //Node构造函数就能指向其他节点,接下来是其他节点指向它,这句是指succ的prev指向新节点 if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; //pred的next指向新节点,不要弄反 size++; modCount++; } LinkBefore()的第二个参数是node(index),作用是找到链表中下表为Index的节点并返回:
Nodenode(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { //index小于size的一半就从头查找,否则从尾查找 Node x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }